Taking cues from a “methodical” Fed
With valuations high and the global economy reopening, fixed income portfolio managers Dan Siluk and Jason England argue that investors should take a methodical approach in assessing what is next for the bond market.

4 minute read
Key takeaways:
- The return of low bond yields has raised the stakes for investors as the global economy continues to reopen.
- The Fed is still the only game in town and few central banks would be willing to raise rates before the US central bank.
- With the global recovery uneven, a dispersion of policy responses creates opportunities for bond investors unconstrained by geography.
The trajectory of interest rates in 2021 has been notable for how rapidly they priced in economic recovery and then, beginning in mid-June, the degree to which that view was tempered. Both instances, in our view, are examples of the market getting ahead of itself. We, too, expected rising rates in the wake of vaccination approvals, economic reopening and the expansion of fiscal stimulus, but by March 2021, US Treasury yields had already climbed to levels we expected to see only at year-end. While this summer’s rally in rates likely reflected inflation being transitory, the unwinding of bearish positions put in place as the global economy reopened also likely played a part as traders sought to stem losses. In both cases, we believe the lesson for investors is – in the parlance of the US Federal Reserve (Fed) – to act in a “methodical” and “orderly” manner, and not get too far ahead of the data.
Looking forward, the path of neither the economy nor monetary policy is set in stone. Policy makers have a needle to thread. On one hand, forward-looking indicators such as US purchasing manager indices and capital goods orders denote a strengthening economy. On the other, nearly seven million US jobs lost during the pandemic have yet to return. Given the Fed’s prioritisation of achieving full employment, and its willingness to allow inflation to run above its 2.0% target to do so, we believe the central bank will continue to err on the side of dovishness.
Policy
Cumulative change in US payrolls since the beginning of the pandemic
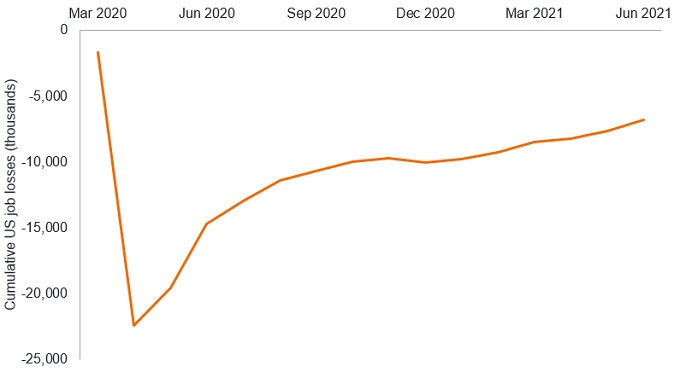
Source: Bloomberg, as of 28 July 2021.
Taper – but no tantrum
By taking this path, the Fed would prove that it learned from past mis-steps, such as what led to 2013’s ‘taper tantrum.’ But unlike the Global Financial Crisis, where markets had to sop up an ocean of bad debt, the recovery from the pandemic finds the global economy on relatively solid footing. As such, we believe – again borrowing from Fed vernacular – a “transparent” plan on tapering assets will soon be put forth, perhaps by the end of the year. Regardless of when an announcement is made, our expectation is that no changes to the Fed’s asset purchase program will occur before the first quarter of 2022.
Transparency does not mean that policy won’t potentially present surprises. Nine years ago, the median estimate of the long-term policy rate by Fed officials was 4.25%. By 2016 it had fallen to 3.0%. It presently sits at 2.5%1. We believe it could go even lower. Driving our view are demographic headwinds and the disinflationary effects of technology. Also likely to exert downward pressure is the expansion of government debt. While this inches toward the Rubicon separating monetary and fiscal policy, Fed officials are keenly aware of the harm that would be caused to government finances should the Treasury have to service current debt loads at borrowing costs closer to their historical average.
Diverging policy – If they can swing it
As is often the case, future US monetary policy will have knock-on effects far from American shores. The management of COVID-19 and its variants have been uneven across geographies. Certain economies are experiencing robust recoveries and others are dealing with rising inflation from surging commodities prices. Even if the rationale for tightening builds, other countries’ central banks would be loath to raise rates before the Fed out of concern about currency appreciation weighing on exports. Despite the sway held by US monetary policy, we believe the dispersion in economic recoveries and policy responses creates opportunities for bond investors willing to cast a wide net. In fact, a geographically diversified bond portfolio may be one of the few tools left for investors attempting to generate income and preserve capital in an otherwise challenging fixed income environment.
Yield on 10-year government bonds
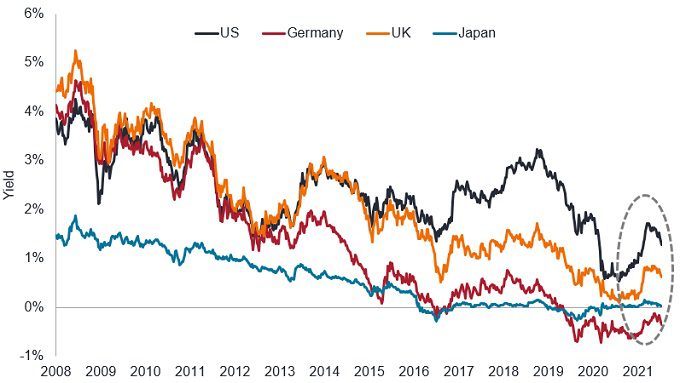
Source: Bloomberg, as of 16 July 2021.
With yields at current levels, only the slightest dip in bond prices can overwhelm coupons, resulting in negative annual returns. Consequently, we believe duration management will be paramount in the months ahead. We believe shorter-dated bonds in countries that may feel compelled to raise rates should be treated with caution while higher-yielding, longer-dated securities could remain stable and possibly enjoy a degree of capital appreciation if inflation indeed proves transitory.
1Source: Bloomberg, US Federal Reserve, as of 28 July 2021
Coupon refers to the periodic interest payments that a bond pays. Duration measures a bond price’s sensitivity to changes in interest rates. The longer a bond’s duration, the higher its sensitivity to changes in interest rates and vice versa. Monetary policy reflects the policies of a central bank, aimed at influencing the level of inflation and growth in an economy. It includes controlling interest rates and the supply of money. Taper tantrum refers to the market’s reaction following the US Federal Reserve Chairman’s comments in May 2013, which suggested that the US was considering tapering (slowing down) the rate of its bond buying programme (quantitative easing). Yield is the level of income on a security typically expressed as a percentage rate. For a bond this is often simply calculated as the total coupons paid in a year divided by the bond price.
These are the views of the author at the time of publication and may differ from the views of other individuals/teams at Janus Henderson Investors. References made to individual securities do not constitute a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security, investment strategy or market sector, and should not be assumed to be profitable. Janus Henderson Investors, its affiliated advisor, or its employees, may have a position in the securities mentioned.
Past performance does not predict future returns. The value of an investment and the income from it can fall as well as rise and you may not get back the amount originally invested.
The information in this article does not qualify as an investment recommendation.
Marketing Communication.
Important information
Please read the following important information regarding funds related to this article.
- An issuer of a bond (or money market instrument) may become unable or unwilling to pay interest or repay capital to the Fund. If this happens or the market perceives this may happen, the value of the bond will fall. High yielding (non-investment grade) bonds are more speculative and more sensitive to adverse changes in market conditions.
- When interest rates rise (or fall), the prices of different securities will be affected differently. In particular, bond values generally fall when interest rates rise (or are expected to rise). This risk is typically greater the longer the maturity of a bond investment.
- Some bonds (callable bonds) allow their issuers the right to repay capital early or to extend the maturity. Issuers may exercise these rights when favourable to them and as a result the value of the Fund may be impacted.
- Emerging markets expose the Fund to higher volatility and greater risk of loss than developed markets; they are susceptible to adverse political and economic events, and may be less well regulated with less robust custody and settlement procedures.
- The Fund may use derivatives to help achieve its investment objective. This can result in leverage (higher levels of debt), which can magnify an investment outcome. Gains or losses to the Fund may therefore be greater than the cost of the derivative. Derivatives also introduce other risks, in particular, that a derivative counterparty may not meet its contractual obligations.
- If the Fund holds assets in currencies other than the base currency of the Fund, or you invest in a share/unit class of a different currency to the Fund (unless hedged, i.e. mitigated by taking an offsetting position in a related security), the value of your investment may be impacted by changes in exchange rates.
- When the Fund, or a share/unit class, seeks to mitigate exchange rate movements of a currency relative to the base currency (hedge), the hedging strategy itself may positively or negatively impact the value of the Fund due to differences in short-term interest rates between the currencies.
- Securities within the Fund could become hard to value or to sell at a desired time and price, especially in extreme market conditions when asset prices may be falling, increasing the risk of investment losses.
- The Fund involves a high level of buying and selling activity and as such will incur a higher level of transaction costs than a fund that trades less frequently. These transaction costs are in addition to the Fund's ongoing charges.
- The Fund could lose money if a counterparty with which the Fund trades becomes unwilling or unable to meet its obligations, or as a result of failure or delay in operational processes or the failure of a third party provider.
- In addition to income, this share class may distribute realised and unrealised capital gains and original capital invested. Fees, charges and expenses are also deducted from capital. Both factors may result in capital erosion and reduced potential for capital growth. Investors should also note that distributions of this nature may be treated (and taxable) as income depending on local tax legislation.
