2022 – optimal conditions for a liquid alternative toolset?

David Elms and Natasha Sibley from the Diversified Alternatives team consider the value of a multi-strategy approach to using liquid alternatives to help improve diversification and complement traditional asset class allocations.
Key takeaways:
- Investors can more naturally diversify away from traditional fixed income and equity exposures at the liquid end of the diversified alternatives spectrum.
- Unlike traditional equities and bond investments, there is no single predominant source of return across alternatives. Instead, we see a more varied range of potentially important tools in the toolkit.
- Correlations tend to rise during periods of market uncertainty. By adding trades that are negatively correlated to the market, investors can achieve a relatively neutral portfolio, even if market conditions suddenly change.
The start of 2022 marked a significant shift in global markets. Inflation, already at elevated levels, moved even higher and became entrenched longer term. The shift from the highly accommodative monetary policy we have become used to from central banks gathered momentum. And more recently, the level of uncertainty gripping the world deepened as the crisis in Ukraine unfolded. It is no surprise then that diversification and downside risk protection, and the potential role that alternatives can play within a wider portfolio, became a key consideration for many investors.
People often think of alternatives as private equity or credit vehicles, more illiquid exposures, early-stage venture equity, or something similar. But the more liquid end of the diversified alternatives spectrum offers investors the opportunity to diversify away from traditional fixed income and equity exposures more naturally. Unlike traditional equities and bonds investments, there is no single predominant source of return across alternatives. Instead of equity or credit risk premia, we see a more varied and often more ephemeral range of potentially important tools in the toolset.
The multi strategy approach
The liquid alternative end of the diversified alternatives space is really dominated by the multi strategy universe. And as the name implies, it is a combination of different ways of trying to generate returns for investors.
There are a wide range of ways to potentially do this. For example, if you think about what investment banks used to do in the 1980s, 1990s and early part of the 2000s, much of the profit generated by the banking industry came from the provision of short-term liquidity to markets. Government bond auctions require a great deal of short-term liquidity, so small discounts appear to encourage investors to provide that liquidity. By taking a systematic approach to the opportunity, it is possible to find interesting sources of return for investors. Similarly, when companies come to market to raise funds, providing the liquidity needed to help a large block of stock find a home can often earn a healthy risk premia.
Another classic strategy is convertible bond arbitrage. Convertible bonds have an implicit embedded volatility exposure. By hedging out the equity risk, credit risk and interest rate risk, it is possible to isolate that volatility exposure, which may be cheap or expensive. That type of exposure can be extremely profitable at the right moment in time.
The rise of price-insensitive products
One of the big themes we have seen in markets in recent times has been the rise of price-insensitive products – the obvious example of which is passive funds. But there has also been a significant increase in bank structured products, ranging all the way from quant investment strategies (QIS) to autocallable notes, typically sold to retail investors.
A more controversial example of price insensitivity activity stems from options trading, where we have seen a sharp increase over the past couple of years, particularly from the US (Exhibit 1). While options trading is not in itself price insensitive, it creates a price insensitive flow as market makers hedge their positions.
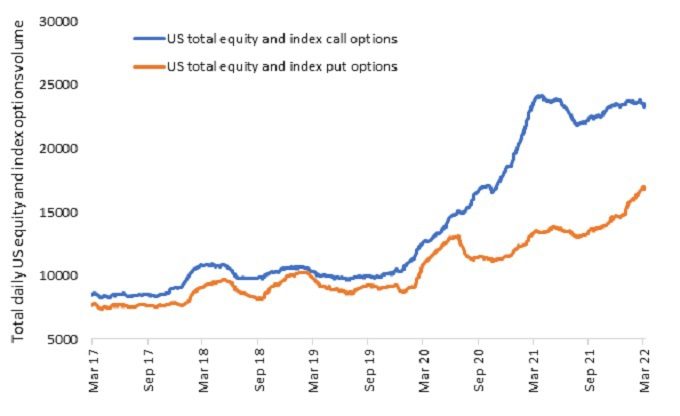
When you combine the increase in price insensitive strategies with a shrinking market share for active asset managers, you end up with price moves that can exhibit more noise (information that confuses or misdirects) and less signal. That can be a good thing for alternative investors as it increases the opportunity set, although it can come with additional volatility.
Flexible, multi-strategy investing
The best way, in our view, to respond to that set of very inflexible trading strategies is to be as flexible as possible, and this is where a multi-strategy approach to alternatives can potentially help. Gaining exposure to a broad range of different strategies, and adjusting that exposure to match the opportunity set, is a real strength, reflected, we think, in the inflows that multi-strategy vehicles have seen in recent years.
Within that multi-strategy concept, there are two ways to proceed, either through the frequency of trading, or by using a lot of different strategies. Ideally, you want strategies that have low correlation, not just to each other but to the market as well. It is important to be cognisant of factor exposure and sector exposure, to ensure that diversification does what it says.
There are a healthy range of liquid alternative options that can be combined or selected for use in a multi-strategy allocation – see Exhibit 2 for examples.
| Equity market neutral: | Seeks to deliver alpha by investing long and short across equities |
| Event driven: | Looks to exploit pricing inefficiencies around corporate events or capital structures |
| Risk transfer: | Looks to capitalise on supply/demand-driven imbalances in the derivatives market. |
| Portfolio protection: | Seeks to mitigate tail risk through a multi-faceted protection strategy |
| Price pressure: | Aims to generate returns through the provision of capital to liquidity opportunities |
| Convertible arbitrage: | Aims to capitalise on mispricings for convertible bonds |
When markets are stressed, correlations can often go to ‘one’
Correlations are not stable at the best of times and in stress scenarios correlations tend to rise in an unfavourable way, sometimes even moving to ‘one’, with all diversification benefits lost. This can be managed by adding hedges; trades that you would expect to be negatively correlated to the market. This means you can create a relatively neutral portfolio, even if market conditions suddenly change, as we saw at the start of 2022.
While hedging comes with a cost, there are two tangible benefits to using it. First is the direct benefit of a lower drawdown when markets are stressed, as we saw in January 2022 when stocks and bonds were both down. The second benefit is they can leave you well placed for what comes after. By smoothing returns through diversification and hedging, investors have an opportunity to add new trades, particularly when other market participants might be unable or unwilling to do the same. The key quality that we believe investors need at times of uncertainty is patience, but also the right tools to provide diversification while other parts of the investment world are failing to deliver as intended.
These are the views of the author at the time of publication and may differ from the views of other individuals/teams at Janus Henderson Investors. References made to individual securities do not constitute a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security, investment strategy or market sector, and should not be assumed to be profitable. Janus Henderson Investors, its affiliated advisor, or its employees, may have a position in the securities mentioned.
Past performance does not predict future returns. The value of an investment and the income from it can fall as well as rise and you may not get back the amount originally invested.
The information in this article does not qualify as an investment recommendation.
Marketing Communication.

