
If one were looking to be entertained by high drama during the past month, rather than tuning into the latest Netflix hit, they could, instead, have clicked on a finance website to keep tabs on the build up to this week’s Fed meeting, with its revolving cast of characters and complex plot twists. In the end, however, the market got what it should have expected all along: A garden-variety conclave where evolving data dictated a garden-variety 25 basis point (bps) rate cut, resulting in a 4.00% to 4.25% band for the benchmark overnight lending rate.
Ever since it paused rate cuts after its December 2024 meeting, the Fed’s rhetoric has centered on the tension between the two components of the central bank’s dual mandate: full employment and price stability. Developments over the past several months, including material downward revisions in payrolls growth and tariffs not sending inflation on a higher trajectory (yet), presented the Fed room to modestly ease still restrictive policy.
While lagging employment and inflation data seemed to validate this decision, those looking for palace intrigue may have noticed the curious – perhaps cognitive – dissonance between the decision to cut rates and a more bullish Summary of Economic Projections which called for higher economic growth and inflation in 2026 along with a slightly lower unemployment rate. While Chairman Jay Powell, in the occasional unsteady performance that the market has come to expect, did not provide an elegant argument squaring this, the Fed likely deserves the benefit of a doubt that political influence was not a factor. After all, the possible successors to Mr. Powell on the open market committee were on board with the decision, leaving the recently inserted understudy, Stephen Miran, as the only dissenter as he opted for a 50-bps reduction.
An evolving – but still resilient – economic backdrop
The state of the U.S. economic expansion has come under question in recent months. Perhaps the major culprit was the downward revision of roughly 900,000 payroll gains in the 12 months through March 2025. This sent the period’s monthly average from a healthy 154,000 to a less healthy 80,000. Furthermore, monthly job gains since April have averaged a paltry 53,000. As Chairman Powell rightfully pointed out, however, payrolls are presently being impacted not only by demand factors but also an unprecedented supply shock due to the Trump administration’s forceful immigration policies.
This shift in labor market dynamics has resulted in a unique situation where jobs could be softening at the same time inflation is proving it’s far from vanquished. The Fed’s preferred gauge of core prices – excluding food and energy – rose from 2.6% in April to 2.9% in July. One argument for this week’s cut is that an overnight lending of 4.5% was well above core inflation, denoting restrictive policy. A rejoinder from the relatively quiet hawkish camp could have been that inflation remains far from the Fed’s 2.0% baseline for price stability. Similarly, market-based expectations based on Treasury inflation protected securities (TIPS) predict inflation averaging 2.47% and 2.39% over the next five and 10 years, respectively. Even the Fed raised its own 2026 core inflation estimate from 2.4% to 2.6% despite somewhat dubiously expecting it to recede to 2.0% only two years later.
Exhibit 1: Fed’s “Dot Plot” survey
Despite seeing economic growth and inflation ticking higher in 2026, the Fed lowered its much-watched “dots” survey of its projected interest rate path for the next two years.
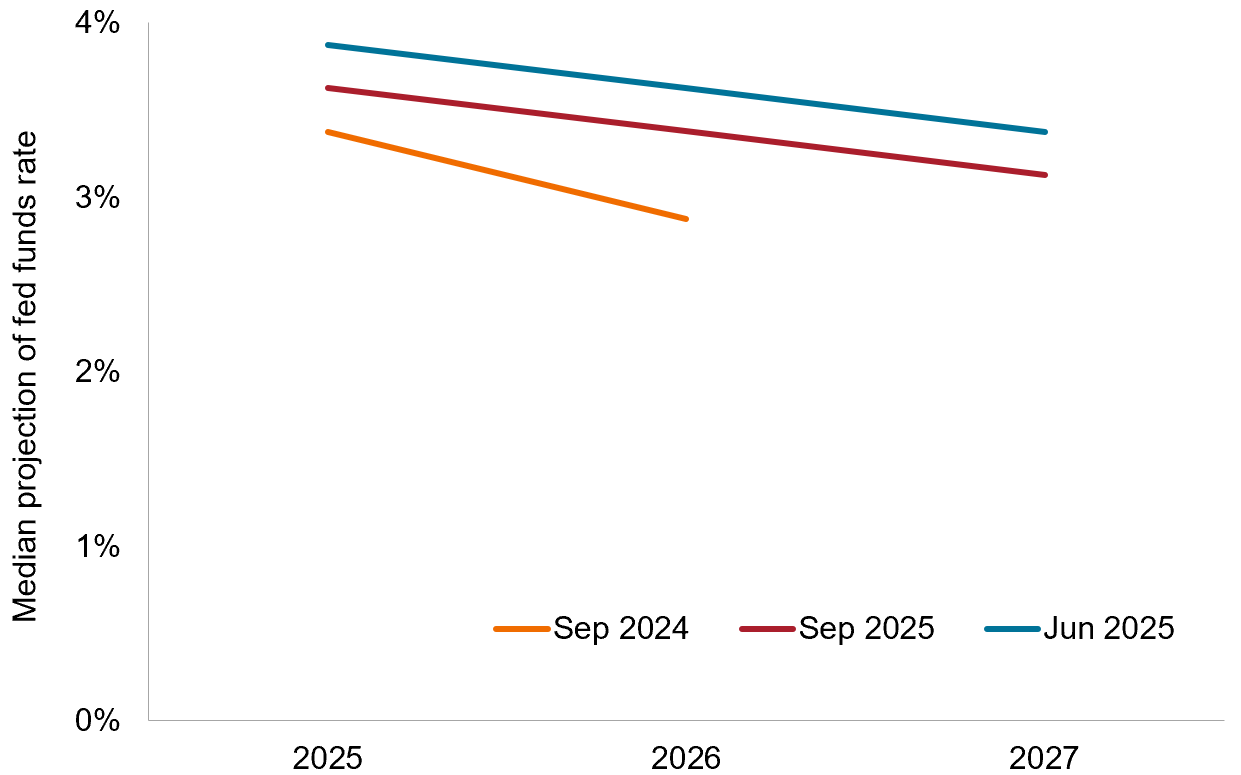
Source: Bloomberg, Janus Henderson Investors, as of 17 September 2025.
What’s worth watching
Part of the reason the Fed chose to halt rate cuts last December was anticipation of the incoming Trump administration’s pro-growth – and potentially inflationary – policies. Among these were deregulation, tax reform and, yes, tariffs. Thus far, companies have been able to either absorb or spread out the tariff hit to where imported goods prices have risen less than expected. To be determined is whether the levies result in a one-off resetting of price levels or trade barriers dampen the competition among companies that tends to benefit consumers. What the Fed wants to avoid, perhaps above all else, is expectations for inflation becoming entrenched well above its 2.0% target.
Unlike 2024 when concerns about slowing growth precipitated 100 bps of rate cuts, with the exception of a clouded labor market, the U.S. economy appears to be on sound footing. Evidence of this is found in a resilient consumer. After its first-quarter hiccup, personal consumption in the second quarter resumed its role in being a key contributor to gross domestic product (GDP). Based on the Atlanta Fed’s GDP Now tracker, this trend has continued deep into the current quarter.
Exhibit 2: GDP
As was the case with second-quarter GDP growth, the Atlanta Fed’s GDP Now tracker shows consumption for both services and goods remaining buoyant in the third quarter.
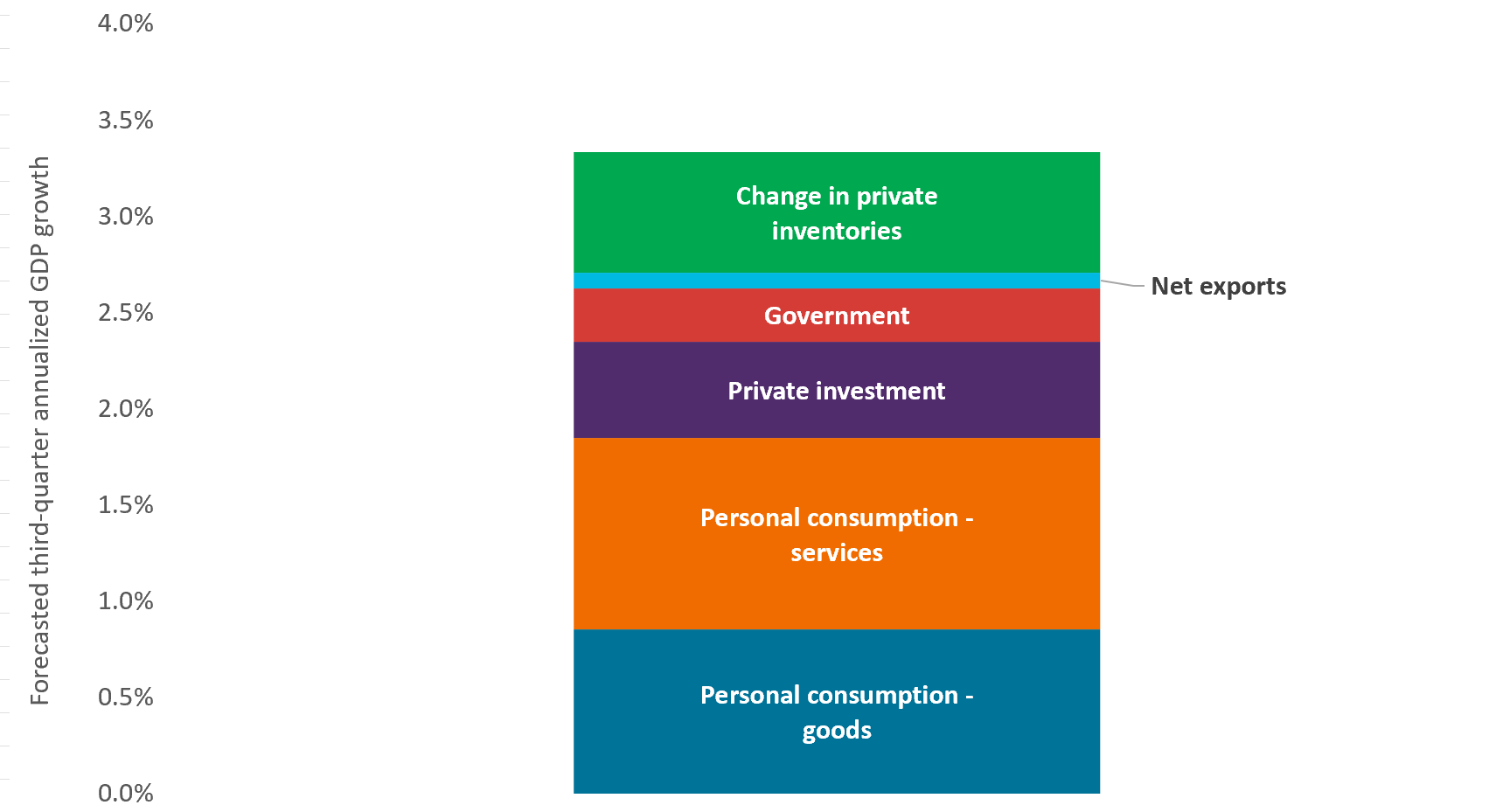
Source: Bloomberg, Atlanta Federal Reserve Bank, Janus Henderson Investors.
Signals from the corporate sector also hint at a continuation of the U.S. economic expansion. Earnings forecasts that tend to reflect underlying economic strength indicate stable growth over the next two years. Company managers are echoing the market’s view in earnings guidance. The predictive power of earnings should hold special sway in the current environment as companies must account for both the appetite of customers to consume and how tariffs may impact operating margins.
Sourcing the right kind of risk, in the right place
With this meeting, the Fed has charted a path for modestly more dovish policy over the next 15 months – and possibly beyond. Given the central bank’s practice of telegraphing policy so as not to catch the market off guard, much of the appreciation associated with a resumption of rate cuts was already reflected in bond prices. While a welcome development – as long as it doesn’t correspond with a rapidly deteriorating economy – compressed yields do present a challenge for investors. We are nowhere near the reach-for-yield era of the 2010s but low rates and rich corporate bond valuations may compel some investors to either extend duration or increase exposure to lower-quality borrowers to compensate for falling yields. We caution against either of these tactics.
Clearly the pendulum has swung away from price stability and toward full employment. But investors should never lose sight of the deleterious effects that inflation can have on fixed income securities, and with the inflation question far from settled in the U.S., we don’t think extending duration in the country to capture incremental yield is worth the risk.
To compensate for lower U.S. yields, investors concerned about generating attractive income and diversifying against riskier assets should seek to expand their fixed income universe. Five years on from the depths of the pandemic, monetary policies have diverged. This creates opportunities for investors to source duration in markets where rates are still likely to fall and increase exposure to more cyclical corporate credits in regions where the hard work of righting the economic ship has already occurred.
Basis point (bp) equals 1/100 of a percentage point. 1 bp = 0.01%, 100 bps = 1%.
Duration measures a bond price’s sensitivity to changes in interest rates. The longer a bond’s duration, the higher its sensitivity to changes in interest rates and vice versa.
Inflation-linked bonds feature adjustments to principal based on inflation rates. They typically have lower yields than conventional fixed-rate bonds and decline in price when real interest rates rise.
Monetary Policy refers to the policies of a central bank, aimed at influencing the level of inflation and growth in an economy. It includes controlling interest rates and the supply of money.
Quantitative Easing (QE) is a government monetary policy occasionally used to increase the money supply by buying government securities or other securities from the market.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Fixed income securities are subject to interest rate, inflation, credit and default risk. The bond market is volatile. As interest rates rise, bond prices usually fall, and vice versa. The return of principal is not guaranteed, and prices may decline if an issuer fails to make timely payments or its credit strength weakens.
Queste sono le opinioni dell'autore al momento della pubblicazione e possono differire da quelle di altri individui/team di Janus Henderson Investors. I riferimenti a singoli titoli non costituiscono una raccomandazione all'acquisto, alla vendita o alla detenzione di un titolo, di una strategia d'investimento o di un settore di mercato e non devono essere considerati redditizi. Janus Henderson Investors, le sue affiliate o i suoi dipendenti possono avere un’esposizione nei titoli citati.
Le performance passate non sono indicative dei rendimenti futuri. Tutti i dati dei rendimenti includono sia il reddito che le plusvalenze o le eventuali perdite ma sono al lordo dei costi delle commissioni dovuti al momento dell'emissione.
Le informazioni contenute in questo articolo non devono essere intese come una guida all'investimento.
Non vi è alcuna garanzia che le tendenze passate continuino o che le previsioni si realizzino.
Comunicazione di Marketing.
Important information
Please read the following important information regarding funds related to this article.
- Gli emittenti di obbligazioni (o di strumenti del mercato monetario) potrebbero non essere più in grado di pagare gli interessi o rimborsare il capitale, ovvero potrebbero non intendere più farlo. In tal caso, o qualora il mercato ritenga che ciò sia possibile, il valore dell'obbligazione scenderebbe.
- L’aumento (o la diminuzione) dei tassi d’interesse può influire in modo diverso su titoli diversi. Nello specifico, i valori delle obbligazioni si riducono di norma con l'aumentare dei tassi d'interesse. Questo rischio risulta di norma più significativo quando la scadenza di un investimento obbligazionario è a più lungo termine.
- Alcune obbligazioni (obbligazioni callable) consentono ai loro emittenti il diritto di rimborsare anticipatamente il capitale o di estendere la scadenza. Gli emittenti possono esercitare tali diritti laddove li ritengano vantaggiosi e, di conseguenza, il valore del Fondo può esserne influenzato.
- Il Fondo potrebbe usare derivati al fine di conseguire il suo obiettivo d'investimento. Ciò potrebbe determinare una "leva", che potrebbe amplificare i risultati dell'investimento, e le perdite o i guadagni per il Fondo potrebbero superare il costo del derivato. I derivati comportano rischi aggiuntivi, in particolare il rischio che la controparte del derivato non adempia ai suoi obblighi contrattuali.
- Qualora il Fondo detenga attività in valute diverse da quella di base del Fondo o l'investitore detenga azioni o quote in un'altra valuta (a meno che non siano "coperte"), il valore dell'investimento potrebbe subire le oscillazioni del tasso di cambio.
- Se il Fondo, o una sua classe di azioni con copertura, intende attenuare le fluttuazioni del tasso di cambio tra una valuta e la valuta di base, la stessa strategia di copertura potrebbe generare un effetto positivo o negativo sul valore del Fondo, a causa delle differenze di tasso d’interesse a breve termine tra le due valute.
- I titoli del Fondo potrebbero diventare difficili da valutare o da vendere al prezzo e con le tempistiche desiderati, specie in condizioni di mercato estreme con il prezzo delle attività in calo, aumentando il rischio di perdite sull'investimento.
- Il Fondo potrebbe perdere denaro se una controparte con la quale il Fondo effettua scambi non fosse più intenzionata ad adempiere ai propri obblighi, o a causa di un errore o di un ritardo nei processi operativi o di una negligenza di un fornitore terzo.
Specific risks
- Gli emittenti di obbligazioni (o di strumenti del mercato monetario) potrebbero non essere più in grado di pagare gli interessi o rimborsare il capitale, ovvero potrebbero non intendere più farlo. In tal caso, o qualora il mercato ritenga che ciò sia possibile, il valore dell'obbligazione scenderebbe.
- L’aumento (o la diminuzione) dei tassi d’interesse può influire in modo diverso su titoli diversi. Nello specifico, i valori delle obbligazioni si riducono di norma con l'aumentare dei tassi d'interesse. Questo rischio risulta di norma più significativo quando la scadenza di un investimento obbligazionario è a più lungo termine.
- Il Fondo investe in obbligazioni ad alto rendimento (non investment grade) che, sebbene offrano di norma un interesse superiore a quelle investment grade, sono più speculative e più sensibili a variazioni sfavorevoli delle condizioni di mercato.
- Alcune obbligazioni (obbligazioni callable) consentono ai loro emittenti il diritto di rimborsare anticipatamente il capitale o di estendere la scadenza. Gli emittenti possono esercitare tali diritti laddove li ritengano vantaggiosi e, di conseguenza, il valore del Fondo può esserne influenzato.
- Il Fondo potrebbe usare derivati al fine di conseguire il suo obiettivo d'investimento. Ciò potrebbe determinare una "leva", che potrebbe amplificare i risultati dell'investimento, e le perdite o i guadagni per il Fondo potrebbero superare il costo del derivato. I derivati comportano rischi aggiuntivi, in particolare il rischio che la controparte del derivato non adempia ai suoi obblighi contrattuali.
- Qualora il Fondo detenga attività in valute diverse da quella di base del Fondo o l'investitore detenga azioni o quote in un'altra valuta (a meno che non siano "coperte"), il valore dell'investimento potrebbe subire le oscillazioni del tasso di cambio.
- Se il Fondo, o una sua classe di azioni con copertura, intende attenuare le fluttuazioni del tasso di cambio tra una valuta e la valuta di base, la stessa strategia di copertura potrebbe generare un effetto positivo o negativo sul valore del Fondo, a causa delle differenze di tasso d’interesse a breve termine tra le due valute.
- I titoli del Fondo potrebbero diventare difficili da valutare o da vendere al prezzo e con le tempistiche desiderati, specie in condizioni di mercato estreme con il prezzo delle attività in calo, aumentando il rischio di perdite sull'investimento.
- Il Fondo potrebbe perdere denaro se una controparte con la quale il Fondo effettua scambi non fosse più intenzionata ad adempiere ai propri obblighi, o a causa di un errore o di un ritardo nei processi operativi o di una negligenza di un fornitore terzo.
- Oltre al reddito, questa classe di azioni può distribuire plusvalenze di capitale realizzate e non realizzate e il capitale inizialmente investito. Sono dedotti dal capitale anche commissioni, oneri e spese. Entrambi i fattori possono comportare l’erosione del capitale e un potenziale ridotto di crescita del medesimo. Si richiama l’attenzione degli investitori anche sul fatto che le distribuzioni di tale natura possono essere trattate (e quindi imponibili) come reddito, secondo la legislazione fiscale locale.