Listed real estate: Weaker shelter inflation the additional signal needed for Fed rate cuts?
Portfolio Managers Guy Barnard & Greg Kuhl highlight how the shelter component of CPI is exerting downward pressure on inflation, paving the way for rate cuts – a tailwind for listed real estate.

5 minute read
Key takeaways:
- Shelter, the largest component of headline CPI, showed an increase of 5.7% for Q1 2024 while the Cleveland Fed’s New Tenant Index, considered a more real-time measure of rent expense, rose by only 0.4%.
- Coupled with the team’s observations and data from residential REITs, this suggests a significant downside in the shelter component of headline CPI over the next 12 months.
- This could be the indicator that the Fed needs to cut rates, and the catalyst for a boost to listed real estate valuations.
As a team of real estate specialists, we typically prefer to refrain from throwing our hat in the ring when it comes to macro. However, given the market’s current focus on inflation, and the fact that shelter is the single largest factor in the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) calculation at around 36% of the total basket, we believe we can add some value to this part of the conversation.
The shelter component of headline CPI is often regarded as backward looking and does not always align with measures considered to be more “real time”. The Cleveland Fed has written extensively on this topic, concluding that “this discrepancy is almost entirely explained by differences in rent growth for new tenants relative to the average rent growth for all tenants”. 1 It produces a quarterly New Tenant Repeat Rent Index, which calculates the change in rents for new tenants only. The distinction between “all tenants versus new tenants” is especially important right now, and warrants further discussion.
JHI
The shelter component of headline CPI showed an increase of 5.7% for Q1 2024 while the Cleveland Fed’s New Tenant Index showed an increase of just 0.4%. According to the Cleveland Fed, “rent inflation for new tenants leads the official (US) Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) rent inflation by four quarters,” suggesting significant downside in the shelter component of headline CPI over the next 12 months (Chart 1). All of this aligns well with our understanding of the US apartment market. Similar to the US Federal Reserve’s data, based on data reported by the listed apartment real estate investment trust (REITs) and our conversations with private residential landlords, rent renewals for tenants staying in place are growing significantly more than those for new leases. In Q1 2024, US listed residential REITs reported an average renewal rent increase of 4.65% and a rental decrease on new leases of 1.25%. While most people prefer not to move every year, in a world where finding out the rent for a new apartment takes nothing more than a Google search, we don’t believe the current wide spread between new and renewal rents is sustainable. Even without an explicit financial incentive, turnover in rental residential has historically ranged from 30-50% per year, meaning that most existing tenants become new tenants somewhat regularly. Ultimately, renewal rents and new rents need to converge, which is essentially what the Cleveland Fed has stated.
Chart 1: Shelter component of CPI vs new tenant rents
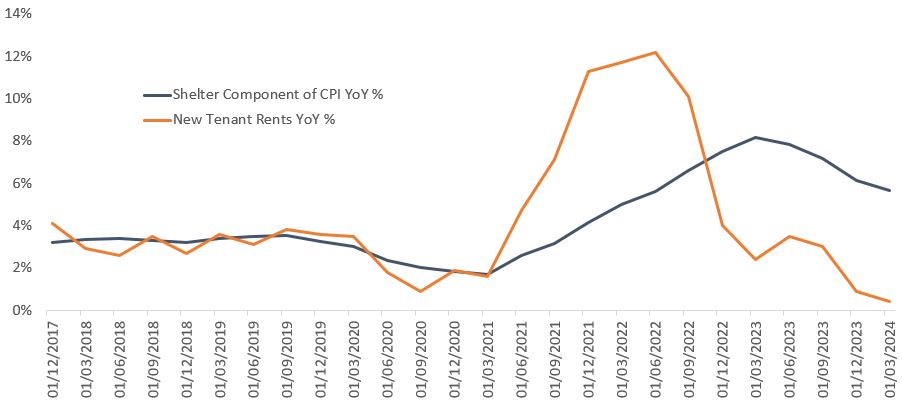
Source: US CPI urban consumers shelter NSA, New Tenant Repeat Rent Index, BLS, Cleveland Fed, Janus Henderson Investors analysis as of 31 March 2024.
Prices of nearly everything have risen quickly and dramatically over the past few years, and some of the historical measuring sticks, like headline CPI, struggle to keep up with the rapidity of changes. In an effort to show where CPI may be headed, we have created an adjusted CPI index where we replace the shelter component of CPI with the Cleveland Fed’s New Tenant Repeat Rent Index. Using this methodology, headline CPI for Q1 2024 would have come in at 1.4%, significantly below the Fed’s 2% target (Chart 2). Holding all else constant, if we believe in the four-quarter lag between new rents and CPI rents, inflation shouldn’t be a concern for very much longer.
Chart 2: Headline CPI vs Headline CPI adjusted for new tenant rents
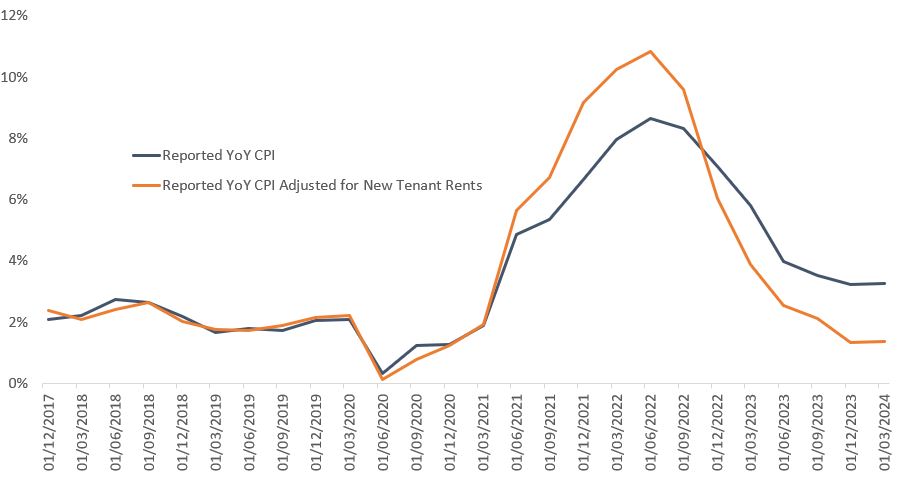
Source: BLS, CPI for all urban consumers YoY non-seasonally adjusted, Consumer Price Index for all urban consumers: all items less shelter YOY NSA, New Tenant Repeat Rent Index, Janus Henderson Investors analysis.
At the Fed’s June press conference, Chair Jerome Powell talked about needing more confidence inflation was making steady progress towards 2% before considering rate cuts. On the same day, monthly CPI came in at 0%. While our team won’t try to make forecasts about the rest of the CPI basket, we do believe the shelter component, with its 36% weighting, is likely going to continue exerting downward pressure on the headline figure. This may be enough to give the Fed the confidence it’s looking for to cut rates, and for investors the assurance to look beyond the macroeconomic uncertainty and refocus on listed real estate’s strong fundamentals – while not a guide to future performance, the sector has historically outperformed following a final Fed hike in a rate-rising cycle.2
1 https://www.clevelandfed.org/publications/working-paper/2022/wp-2238-disentangling-rent-index-differences
2 UBS, Datastream, Janus Henderson analysis, as at 31 December 2022. Past performance does not predict future returns.
Headline CPI is a measure that examines the price change of a basket of consumer goods and services over time. It is used to estimate inflation. ‘Headline’ CPI inflation is a calculation of total inflation in an economy, and includes items such as food and energy, where prices tend to be more volatile. ‘Core’ CPI inflation is a measure of inflation that excludes transitory/volatile items such as food and energy.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
REITs or Real Estate Investment Trusts invest in real estate, through direct ownership of property assets, property shares or mortgages. As they are listed on a stock exchange, REITs are usually highly liquid and trade like shares.
Real estate securities, including Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), are sensitive to changes in real estate values and rental income, property taxes, interest rates, tax and regulatory requirements, supply and demand, and the management skill and creditworthiness of the company. Additionally, REITs could fail to qualify for certain tax-benefits or registration exemptions which could produce adverse economic consequences.
These are the views of the author at the time of publication and may differ from the views of other individuals/teams at Janus Henderson Investors. References made to individual securities do not constitute a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security, investment strategy or market sector, and should not be assumed to be profitable. Janus Henderson Investors, its affiliated advisor, or its employees, may have a position in the securities mentioned.
Past performance does not predict future returns. The value of an investment and the income from it can fall as well as rise and you may not get back the amount originally invested.
The information in this article does not qualify as an investment recommendation.
There is no guarantee that past trends will continue, or forecasts will be realised.
Marketing Communication.
Important information
Please read the following important information regarding funds related to this article.
- Shares/Units can lose value rapidly, and typically involve higher risks than bonds or money market instruments. The value of your investment may fall as a result.
- The Fund is focused towards particular industries or investment themes and may be heavily impacted by factors such as changes in government regulation, increased price competition, technological advancements and other adverse events.
- This Fund may have a particularly concentrated portfolio relative to its investment universe or other funds in its sector. An adverse event impacting even a small number of holdings could create significant volatility or losses for the Fund.
- The Fund invests in real estate investment trusts (REITs) and other companies or funds engaged in property investment, which involve risks above those associated with investing directly in property. In particular, REITs may be subject to less strict regulation than the Fund itself and may experience greater volatility than their underlying assets.
- The Fund may use derivatives with the aim of reducing risk or managing the portfolio more efficiently. However this introduces other risks, in particular, that a derivative counterparty may not meet its contractual obligations.
- If the Fund holds assets in currencies other than the base currency of the Fund, or you invest in a share/unit class of a different currency to the Fund (unless hedged, i.e. mitigated by taking an offsetting position in a related security), the value of your investment may be impacted by changes in exchange rates.
- Securities within the Fund could become hard to value or to sell at a desired time and price, especially in extreme market conditions when asset prices may be falling, increasing the risk of investment losses.
- The Fund could lose money if a counterparty with which the Fund trades becomes unwilling or unable to meet its obligations, or as a result of failure or delay in operational processes or the failure of a third party provider.